What is Optical Fiber?
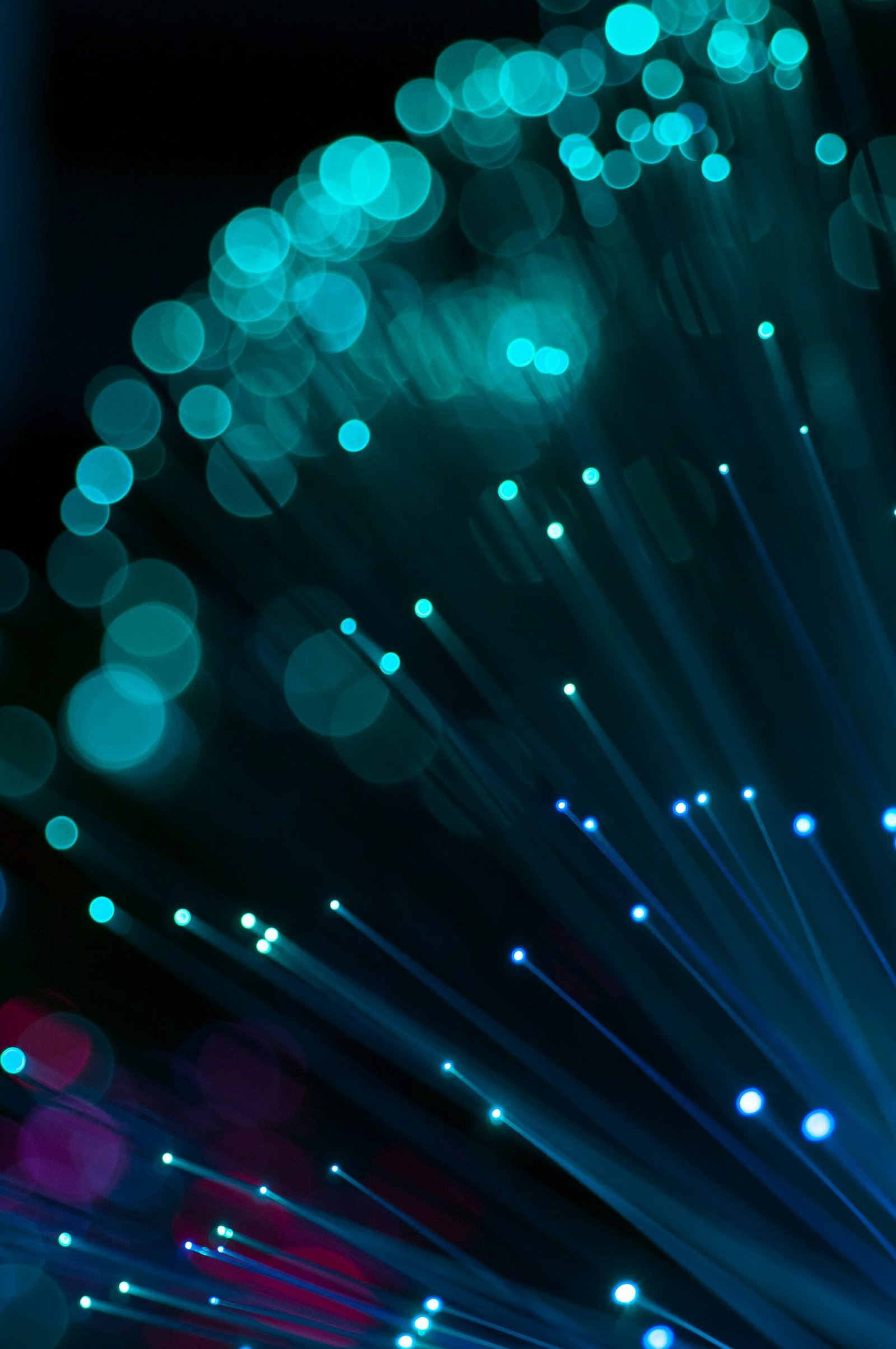
Optical fiber, also known as fiber optic cable, is a type of telecommunications medium that is used to transmit information in the form of light pulses. It consists of a thin, flexible strand of glass or plastic that is capable of carrying large amounts of data over long distances.
The concept of optical fiber communication dates back to the 19th century, but it wasn’t until the late 20th century that it became a practical and widely used technology. Today, optical fiber is the backbone of modern telecommunications networks, enabling high-speed internet connections, long-distance telephone calls, and cable television transmission.
How does optical fiber work?
Optical fiber works on the principle of total internal reflection. The core of the fiber, which is the central part through which the light travels, has a higher refractive index than the cladding, which is the outer layer surrounding the core. This difference in refractive index causes the light to bounce off the boundary between the core and the cladding, keeping it trapped within the core and allowing it to travel long distances without significant loss of signal.
At each end of the fiber, there are devices called transmitters and receivers. The transmitter converts electrical signals into light pulses, which are then sent through the fiber. The receiver at the other end converts the light pulses back into electrical signals, which can be understood by computers, phones, or other devices.
Advantages of optical fiber
Optical fiber offers several advantages over traditional copper cables:
- High bandwidth: Optical fiber has a much higher bandwidth than copper cables, allowing for faster and more efficient data transmission.
- Long-distance transmission: Optical fiber can transmit data over much longer distances without the need for signal boosters or repeaters.
- Immunity to electromagnetic interference: Unlike copper cables, optical fiber is not affected by electromagnetic interference from nearby power lines or other sources.
- Security: Optical fiber is difficult to tap into, making it more secure for transmitting sensitive information.
- Lightweight and flexible: Optical fiber cables are lightweight and flexible, making them easier to install and manage.
Applications of optical fiber
Optical fiber is used in a wide range of applications, including:
- Telecommunications: Optical fiber forms the backbone of telecommunications networks, enabling high-speed internet connections, long-distance telephone calls, and cable television transmission.
- Data centers: Optical fiber is used to connect servers and storage devices within data centers, allowing for fast and reliable data transfer.
- Medical imaging: Optical fiber is used in medical imaging devices such as endoscopes and laparoscopes, allowing doctors to see inside the body without invasive surgery.
- Sensor networks: Optical fiber can be used in sensor networks to monitor and transmit data from remote locations, such as in environmental monitoring or industrial applications.
- Defense and security: Optical fiber is used in military and security applications for secure communication and surveillance systems.
Conclusion
Optical fiber is a crucial technology that has revolutionized the way we communicate and transmit data. Its high bandwidth, long-distance transmission capabilities, and immunity to electromagnetic interference make it an ideal choice for modern telecommunications networks. As technology continues to advance, optical fiber will play an increasingly important role in enabling faster and more reliable communication.